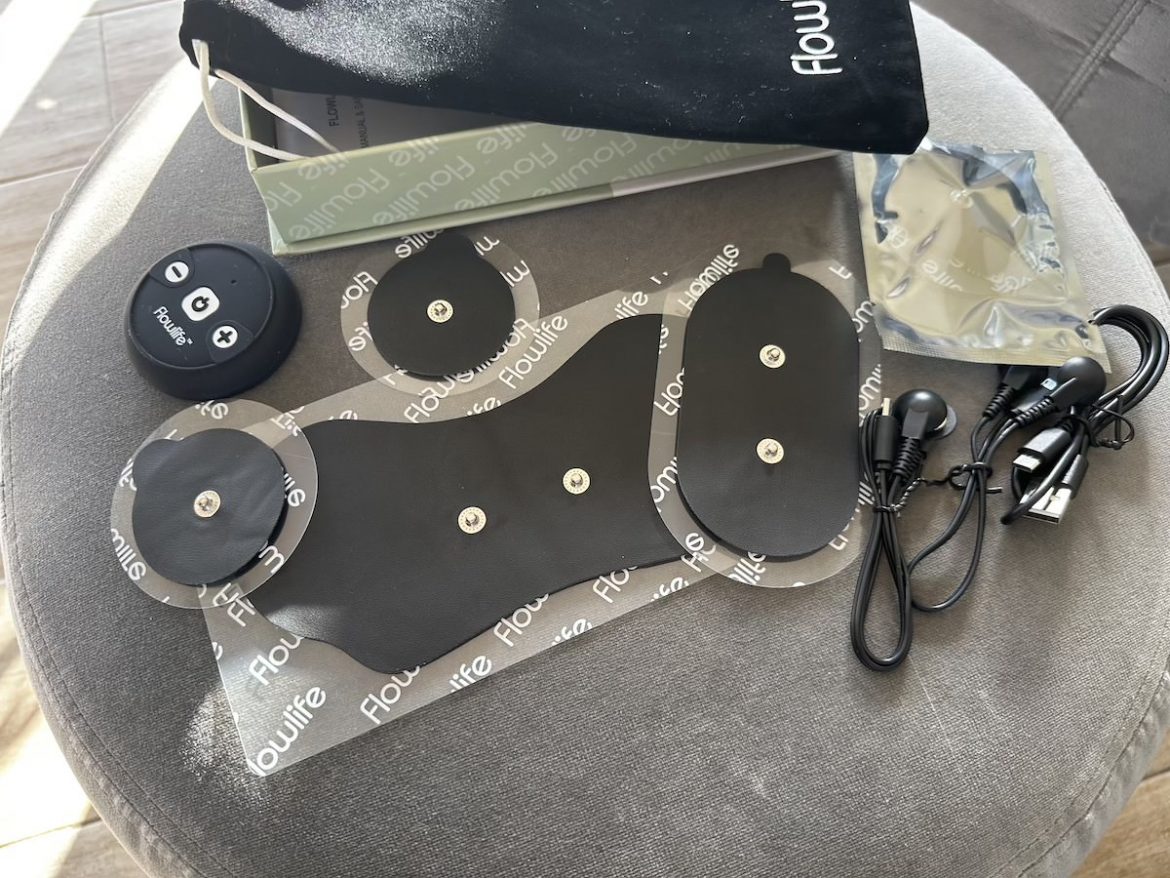
Pain, an unwelcome companion that can disrupt our daily lives, is a common experience affecting individuals across ages and demographics. From the dull ache of chronic conditions to the sharp throb of acute injuries, pain can significantly impact our mobility, sleep, and overall well-being. While medication remains a cornerstone of pain management, the search for alternative, non-invasive therapies continues to evolve. Here I will delve into the topic of TENS for Pain Relief and Recovery.
Enter transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), a non-pharmaceutical approach that harnesses the power of electrical currents to alleviate pain. This innovative therapy, often administered via handheld devices, has gained widespread recognition for its ability to provide effective pain relief without the reliance on medications.
In this article, I will embark on a journey to explore the world of TENS, delving into its mechanisms of action, benefits, and potential applications. We will unravel the science behind this remarkable technology and examine its versatility in addressing a range of pain conditions.
Read more: Best recovery tools for runners
What is TENS?
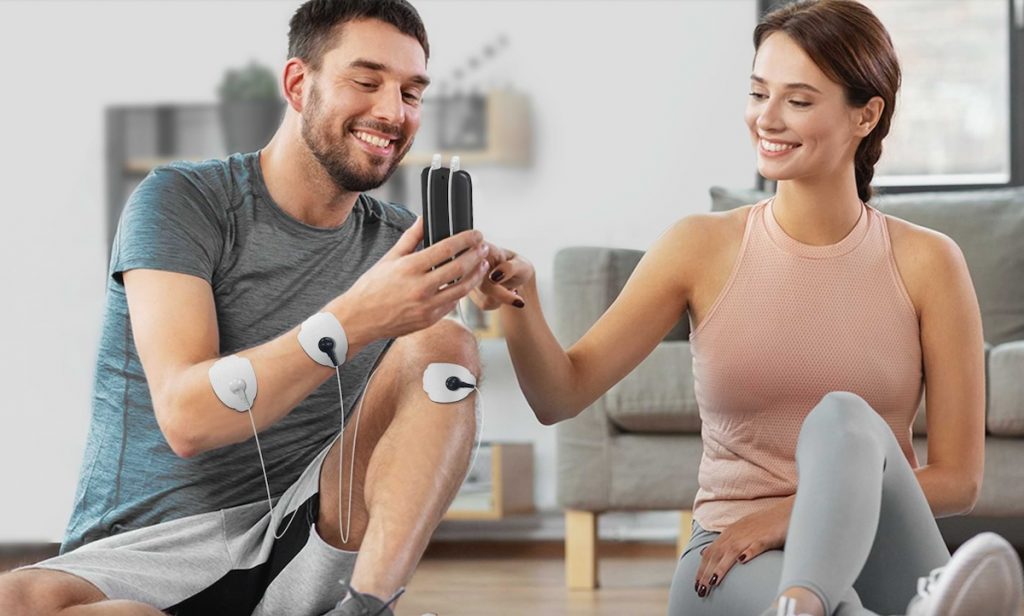

Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) is a non-invasive, drug-free pain relief therapy that uses mild electrical currents to stimulate the nerves beneath the skin. A TENS unit, a small, hand-held device, generates the electrical currents, which are delivered through self-adhesive electrode pads placed on the skin near the painful area.
The electrical stimulation can block pain signals from reaching the brain, or it can activate the body’s natural pain-relieving mechanisms, such as the release of endorphins.
How does TENS work?


TENS works in two ways:
- Gate Control Theory: The electrical stimulation activates inhibitory sensory neurons, which send signals to the spinal cord that block pain signals from reaching the brain.
- Endorphin Release: The electrical stimulation triggers the release of endorphins, which are the body’s natural pain relievers.
What are the pros and cons of TENS?
Pros:
- Non-invasive and drug-free
- Effective for a variety of pain conditions, including arthritis, back pain, neck pain, muscle pain, and menstrual cramps
- Can be used at home or on the go
- Relatively inexpensive
Cons:
- May not be effective for all pain conditions
- May cause some mild side effects, such as tingling, numbness, or muscle twitching
- May not be suitable for people with certain medical conditions, such as implanted medical devices or heart problems
Who is TENS for?
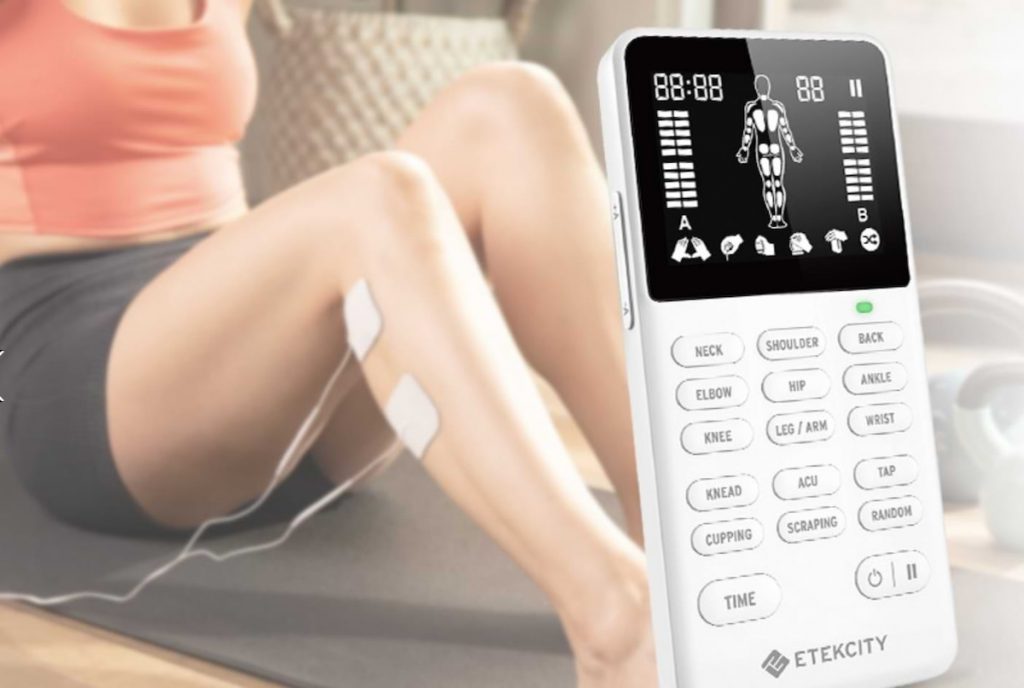

TENS is a safe and effective treatment for many people with pain. It is a good option for people who are looking for a non-invasive, drug-free way to manage their pain. TENS is often used in conjunction with other pain management treatments, such as physical therapy or medication.
How to use TENS
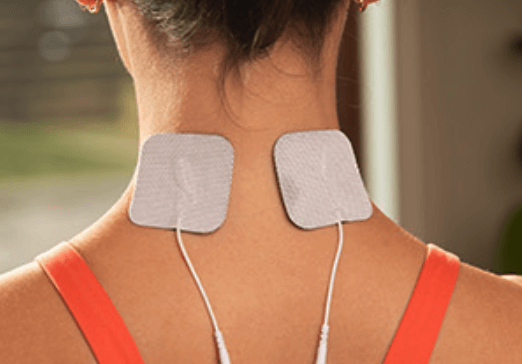
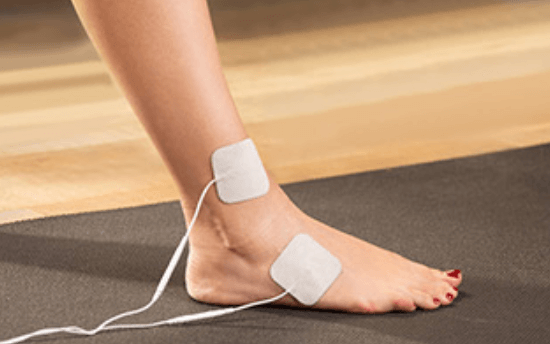
TENS units are typically easy to operate. They have preset programs that you can choose from, or you can customize the settings to your own preferences.
The electrodes should be placed on the skin near the painful area, and the intensity of the electrical stimulation should be adjusted to a comfortable level.
TENS is a safe and effective treatment for many people with pain. If you are interested in trying TENS, talk to your doctor or physical therapist. They can help you determine if TENS is right for you and show you how to use it properly.
Research on the Efficacy of TENS
Numerous studies have been conducted to investigate the effectiveness of TENS for various pain conditions. A systematic review and meta-analysis published in BMJ Open in 2021 analyzed data from 381 studies involving over 35,000 participants.
The review found that TENS was effective in reducing pain intensity compared to placebo in both acute and chronic pain conditions. Additionally, TENS was associated with minimal adverse effects.
Research on the Mechanisms of TENS
The exact mechanisms by which TENS relieves pain are not fully understood, but several theories have been proposed. One theory suggests that TENS activates large diameter, non-painful nerve fibers (A-beta fibers), which inhibit the transmission of pain signals through the spinal cord.
Another theory suggests that TENS releases endorphins, the body’s natural pain relievers.
FAQs About TENS for Pain Relief and Recovery
TENS stands for transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation. It is a non-invasive pain relief therapy that uses mild electrical impulses to block pain signals from reaching the brain.
TENS works by stimulating nerve fibers near the surface of the skin. These nerve fibers send signals to the spinal cord and brain. When the brain receives these signals, it interprets them as non-painful, which can help to reduce or block pain perception.
TENS is a versatile pain relief therapy that can be effective for a variety of conditions, including:
Chronic pain: such as low back pain, arthritis pain, and fibromyalgia
Acute pain: such as muscle pain, pain from injuries, and menstrual cramps
Neuralgia: such as post-herpetic neuralgia and diabetic neuropathy
TENS therapy sessions typically last 20-30 minutes. However, you can use a TENS unit for as long as needed to manage your pain. Some people find that they need to use TENS daily, while others may only use it occasionally.
TENS is generally safe and well-tolerated. Most people do not experience any side effects. However, some people may experience mild side effects such as skin irritation, muscle twitching, or a tingling sensation.
Coverage for TENS therapy varies depending on your insurance plan. Some insurance plans may cover the cost of a TENS unit, while others may only cover a portion of the cost. It is always a good idea to check with your insurance provider before purchasing a TENS unit.





